Environmental Protection
As work to tackle global issues such as global warming and resource depletion advances, shifts in the structure of industry are becoming more apparent. At the Nippon Soda Group, in addition to helping solve these challenges facing society by creating new value through the power of chemistry, we are engaging in environmental protection activities to minimize the negative impact of our own business. By ensuring the continuous development of our business through such initiatives, we are aiming to achieve a sustainable society and improve our corporate value.
- Responses to climate change issues
We support the Paris Agreement and will take action to reduce our greenhouse gas emissions by transitioning to renewable energy and promoting energy conservation, with the aim of achieving carbon neutrality by 2050. - Compliance with environmental laws and regulations
We are committed to environmental protection through compliance with environmental laws and regulations. - Construction of an environmental management system
At our Nippon Soda plants, we have put in place and operate an environmental management system (EMS) compliant with the international standard ISO 14001. By establishing manufacturing processes that reduce our environmental footprint and conserve energy, we endeavor to ensure a balance between environmental conservation and high productivity. - Promotion of resource recycling
We recognize that the sustainable use of Earth’s finite resources is a critical issue affecting the management of the Company. Therefore, we will take measures to conserve resources and maximize resource efficiency, while also reducing waste emissions and promoting recycling. - Prevention of environmental pollution
We do our utmost to cut emissions of environmental pollutants, as well as limit air pollution caused by exhaust gases during processes from raw material intake to storage, manufacturing, and transportation. - Water resources conservation
We take a variety of measures to promote the sustainable use of water resources. These include reducing water consumption, wastewater discharge, and wastewater treatment volumes; preventing water pollution; and developing products and technologies that are water-resource conscious. We also work to identify regions within our supply chain with elevated water risks and take concrete steps to reduce water consumption in those areas. - Preservation of biodiversity
We assess and reduce the impacts of our business activities on biodiversity and ecosystems, and promote conservation activities.
FY 2025/3 targets and achievements levels (KPIs)
(Achievement levels ◎:≥ 90% ○:80-90% △:60-80% ×: ≤ 60%) Red text: KPIs
Responses to Climate Change Issues
Efforts to prevent global warming are critical. Nippon Soda participates in the Keidanren Carbon Neutrality Action Plan, a voluntary action plan promoted by Keidanren (Japan Business Federation). Under the action plan, we are promoting energy saving to achieve the greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions reduction targets.
We have also set medium- to long-term reduction targets, aiming to reduce the Group’s GHG emissions by 20% or more by FY 2026/3 (compared with FY 2014/3), reduce Scope 1 and 2 emissions by 42% or more and Scope 3 emissions by 25% or more by FY 2031/3 (compared with FY 2023/3), and achieve net-zero Scope 1, 2, and 3 emissions by FY 2051/3.
Reduction of energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions
We are engaged in a wide range of measures to reduce our energy intensity. These efforts include replacing our aging equipment with high-efficiency equipment, streamlining and increasing labor efficiency in our production process, and implementing energy-saving measures. Furthermore, we use the Ministry of the Environment’s Basic Guidelines on Accounting for Greenhouse Gas (GHG) Emissions Throughout the Supply Chain when calculating GHG emissions from our business activities (Scope 1, Scope 2) as well as indirect emissions from outside our business activities (Scope 3). In this way, we work to reduce emissions throughout the supply chain.
Energy consumption (in crude oil equivalent)
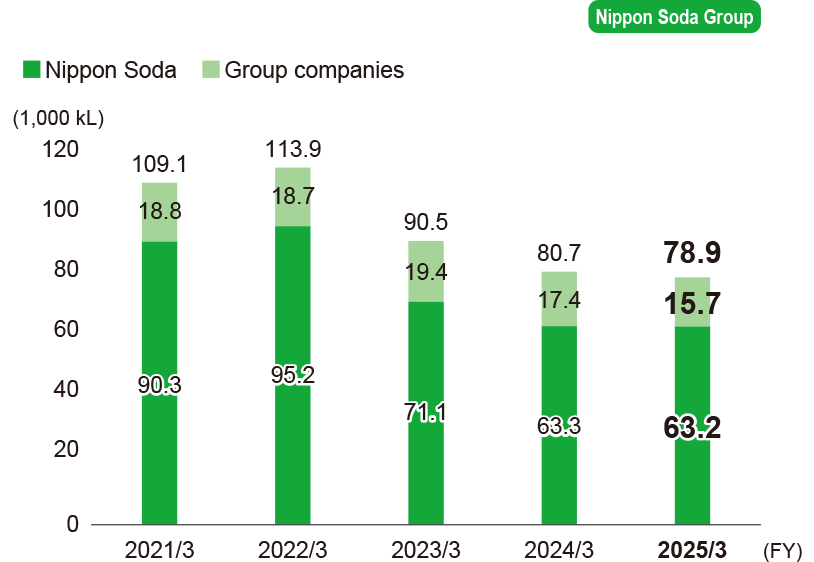
-
* Calculations cover the following.
Nippon Soda: Head Office, four plants, one research center, and six sales offices.
Domestic manufacturing group companies: Nisso Metallochemical Co., Ltd., Nisso Fine Co., Ltd., Shinfuji Kaseiyaku Co., Ltd.
Domestic non-manufacturing group companies: Nisso Shoji Co., Ltd., Sanwa Soko Co., Ltd., Nisso Engineering Co., Ltd., Nisso Kensetsu Co., Ltd., Nisso Green Co., Ltd.
Overseas manufacturing group companies: Nisso Namhae Agro Co., Ltd.
Greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions (Scope 1 and 2)
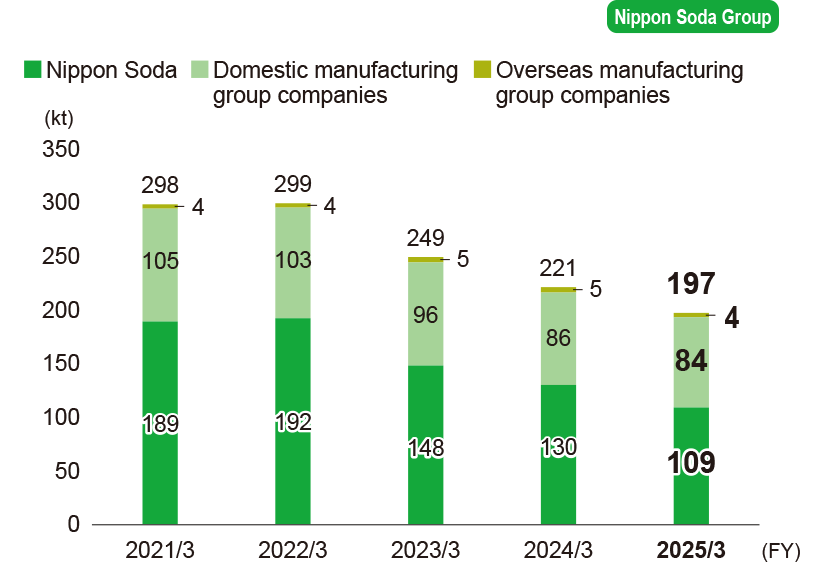
-
* Calculations cover the following.
Nippon Soda: Head Office, four plants, one research center, and six sales offices.
Domestic manufacturing group companies: Nisso Metallochemical Co., Ltd., Nisso Fine Co., Ltd., Shinfuji Kaseiyaku Co., Ltd.
Overseas manufacturing group companies: Nisso Namhae Agro Co., Ltd.
Change in greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions by scope (Scope 1 and 2)
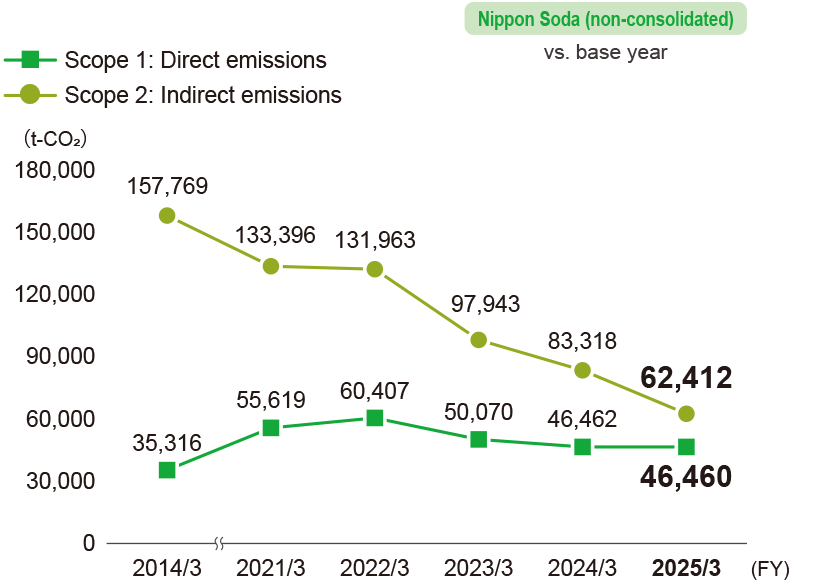
- * Calculations cover Nippon Soda’s Head Office, four plants, one research center, and six sales offices.
Change in energy intensity
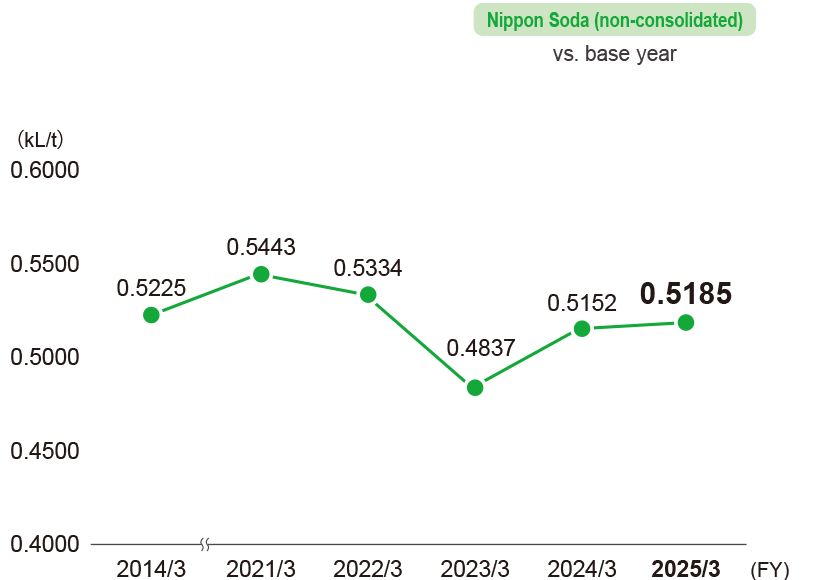
- * For the Nihongi Plant and Chiba Plant we have used the “standard product conversion method,” and for the Takaoka Plant and Mizushima plant the “simple production output method.” Calculations cover Nippon Soda’s Head Office, four plants, one research center, and six sales offices.
Greenhouse Gas Emissions throughout the Supply Chain
Scope 1 emissions 46,460t-CO2
Scope 2 emissions 62,412t-CO2
Scope 3 emissions 164,305t-CO2
| Categories of Scope 3 | Emissions by category |
|---|---|
| Purchased raw materials / services | 135,758t-CO2 |
| Capital goods | 23,339t-CO2 |
| Fuel, etc., not included in Scope 1 or 2 | Not calculated |
| Transport, delivery (upstream) | 3,155t-CO2 |
| Waste generated from business | Not calculated |
| Business trips | 1,773t-CO2 |
| Employee commuting | 280t-CO2 |
| Leased assets (upstream) | None |
| Transport and delivery (downstream) | Not calculated |
| Processing of sold products | Not calculated |
| Use of sold products | Not calculated |
| Disposal of sold products | Not calculated |
| Leased assets (downstream) | None |
| Franchise | None |
| Investment | Not calculated |
- Note: Figures are calculated based on the Ministry of the Environment’s “Emission Factor Database for calculating greenhouse gas emissions, etc., by organizations throughout the supply chain (ver. 3.5).”
Actions to conform to the Fluorocarbons Emission Control Act
To comply with the Fluorocarbons Emission Control Act, we implement periodic inspections by those with expertise, simplified inspections by inspection managers, measures to prevent fluorocarbon emissions, and other required activities at one worksite at a time.
Calculated emissions of fluorocarbons
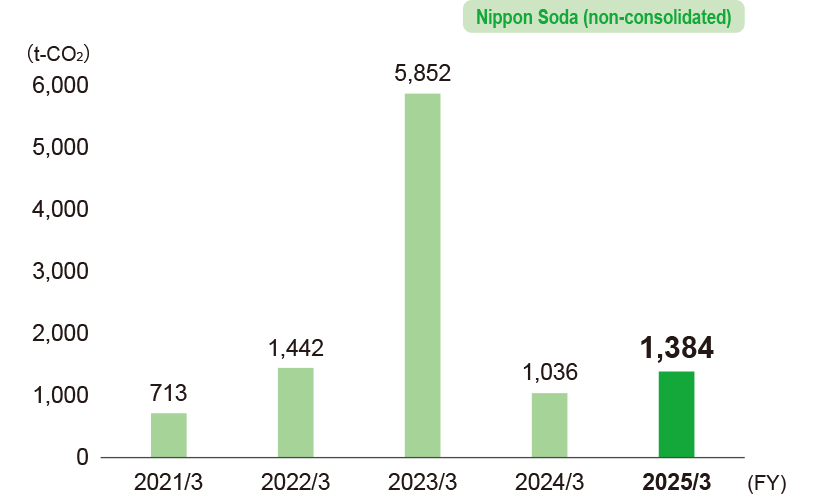
- * Calculations cover Nippon Soda’s Head Office, four plants, one research center, and six sales offices.
- Note: In FY 2023/3, emissions in CO2 equivalent increased due to the additional filling of large-scale equipment using refrigerant with high global warming potential.
Forestry activities and CO2 absorption
Forests play key roles as carbon sinks in the prevention of climate change. Nisso Shoji Co., Ltd. owns approximately 56 hectares of land near the headwaters of the Keta River, a tributary of the Tenryu River. Here, based on afforestation and superficies rights agreements, Shizuoka Prefecture is engaged in the creation and management of a manmade Japanese cedar and cypress forest. In addition to being designated a headwater conservation forest, the forest has also acquired FSC* certification in recognition of sustainable forest management. In this way, the Group is contributing to healthy forest development.
- * The Forest Stewardship Council® is an international non-profit organization that aims to promote responsible management of forests worldwide.
FSC certification shows that an independent third-party organization has recognized that appropriate management systems are in place to ensure forest conservation.
Use of renewable energy
At the Nihongi Plant, we draw industrial water from a nearby river and use the difference in elevation when returning it to the river for small-scale hydroelectric power generation. Since its construction in 1940, the plant has been effectively using this energy in its production activities. Moving forward, we will carefully maintain the power generation facilities at the plant as a stable source of renewable energy.
We purchase renewable electricity to help reduce our GHG emissions. At the Takaoka Plant, in FY 2024/3, we replaced the equivalent of 10% of electricity used in the plant with renewable electricity, which we increased to 20% in FY 2025/3. Going forward, we plan to continue increasing this ratio further. In addition, at the Nihongi Plant, starting in FY 2025/3, we have replaced 100% of the electricity used within the plant with power derived from renewable energy sources.
At the Chiba Plant, we installed solar panels within the plant grounds in the second half of FY 2025/3. The installation of solar power generation systems will enable an annual reduction in CO2 emissions of 1,140 t.
In January 2024, the JP Tower, where our Head Office is located, introduced the Green Basic Plan* offered by TEPCO Energy Partner, Inc. This will ensure net-zero CO2 emissions from electricity used at the building.
Moving forward, we will accelerate our efforts for decarbonization through further examinations of the introduction of renewable energy at other worksites.
- * Green Basic Plan: An electricity plan from TEPCO Energy Partner, Inc. that supplies electricity derived from renewable energy sources such as solar, wind, and hydro power, to ensure net-zero CO2 emissions.
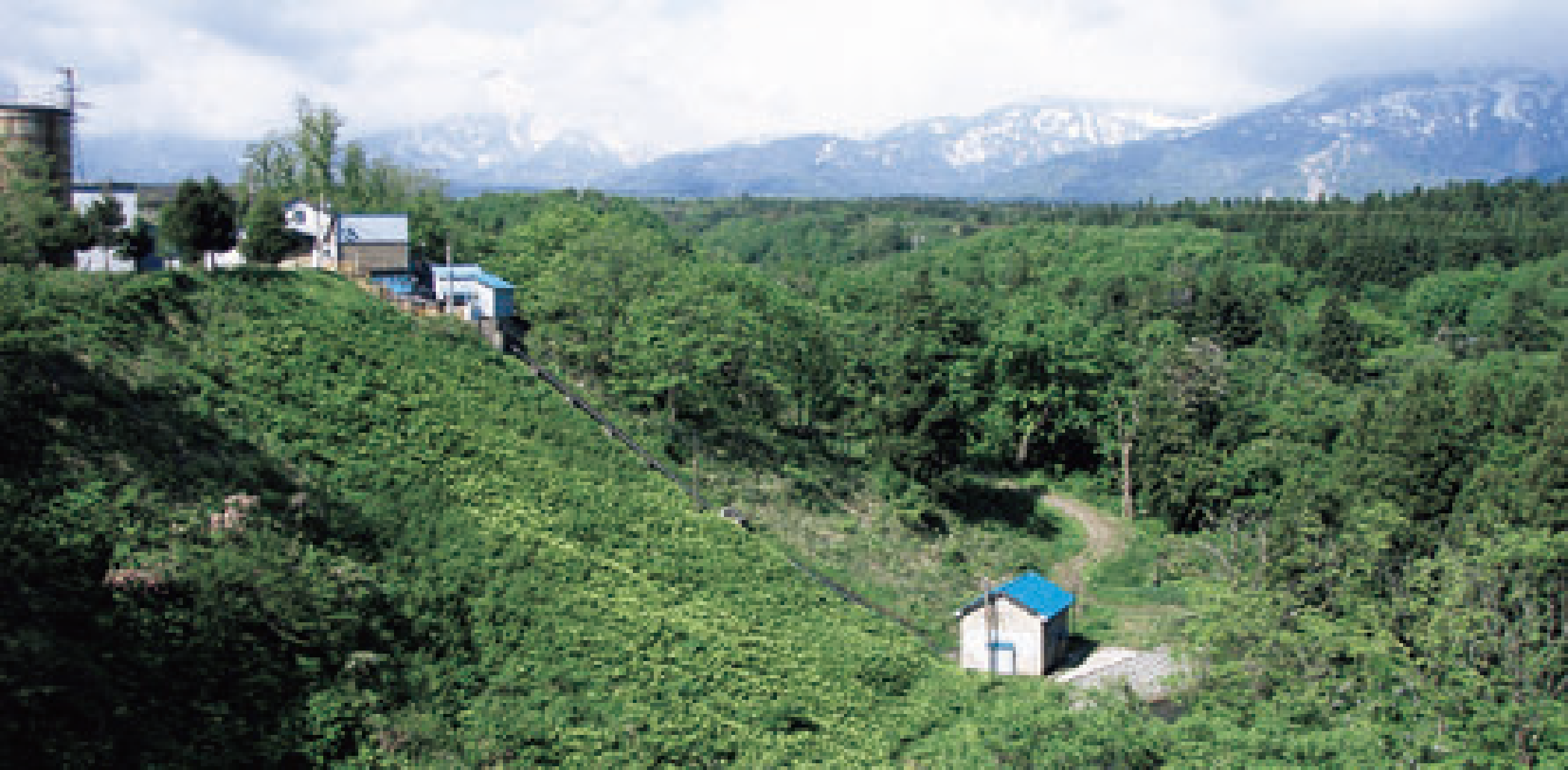

Small hydropower facilities of the Nihongi Plant
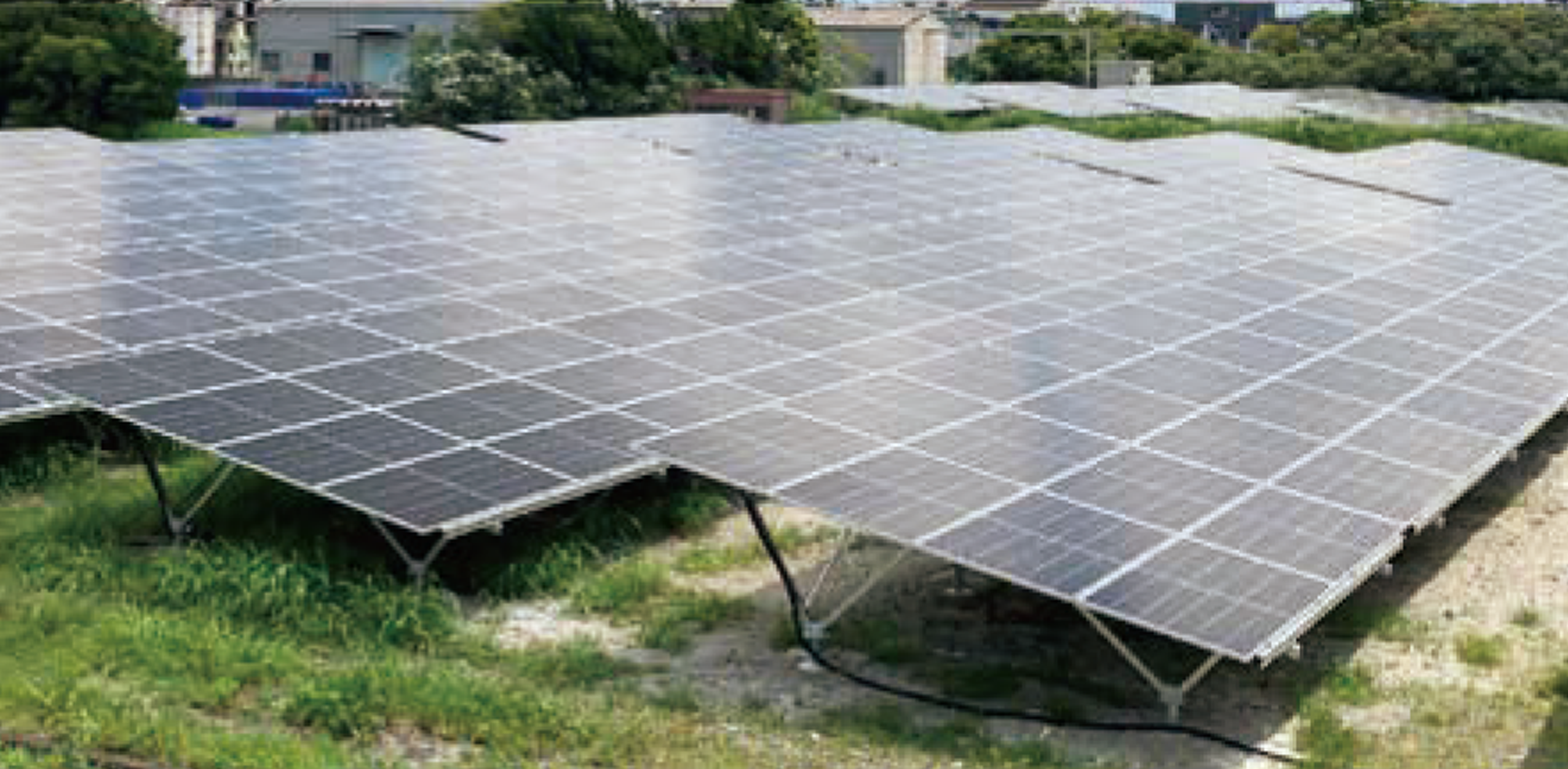

Solar panels at the Chiba Plant
Promotion of energy saving by the Logistics Department
At Nippon Soda, we are working to reduce the energy intensity in our Logistics Department. In FY 2025/3, we undertook a modal shift, in which we switched product transportation from the Takaoka Plant (Toyama Prefecture) to various locations from dedicated truck transport to rail transport. This move not only resulted in a reduction of 472 metric tons (73%) in CO2 emissions but also ensured a stable transportation capacity in response to the so-called 2024 problem, when there was a shortage of truck drivers, and helped streamline the labor-intensive task of securing trucks, which previously required significant time and effort.
Furthermore, we received recognition as a business operator that has succeeded in significantly reducing its environmental impact, saving energy, and improving transport efficiency. Together with Seino Transportation Co., Ltd., we were awarded the Encouragement Prize at the 26th Logistics Environment Awards hosted by the Japan Association for Logistics and Transport.
We will continue working to improve logistics efficiency and reduce environmental burden through measures such as modal shifts in transportation, reducing the frequency of trips by using larger transport containers, and adjusting distribution routes. In 2013, our modal shift initiatives were highly acclaimed, and we were certified with the Eco Rail Mark from the Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism.
Energy consumption and energy intensity related to transport
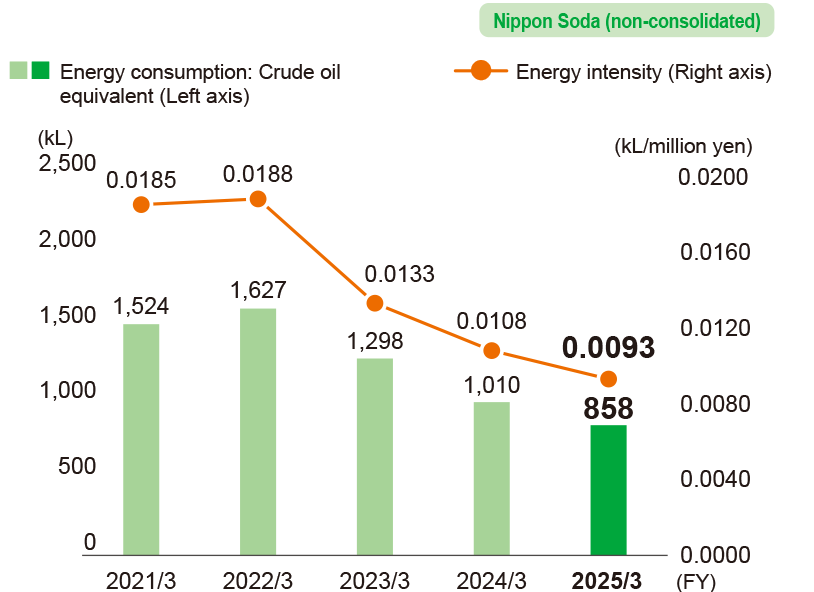
- * Calculations cover Nippon Soda’s Head Office, four plants, one research center, and six sales offices.

Effective Use of Resources and Reduction of Industrial Waste
We participate in the Voluntary Action Plan for Establishing a Sound Material-Cycle Society promoted by Keidanren (Japan Business Federation). Under the action plan, we promote industrial waste reduction to achieve the target amount of reduction in the final disposal of industrial waste at landfill.
Proper management of industrial waste and reduction of the final disposal of industrial waste at landfill
As one of its efforts to help build a sound material-cycle society, Nippon Soda reduces the amount of industrial waste emissions from a long-term perspective and, at the same time, promotes the recycling of industrial waste items and implements other measures to reduce the final disposal amount of industrial waste at landfill.
Zero emissions
In FY 2025/3, Nippon Soda continued to achieve zero emissions.* We will promote the further reduction of industrial waste to continue achieving zero emissions.
- * When the ratio of the amount of final disposal of industrial waste at landfill compared with the amount transported to the industrial waste disposal facility is small. We define “Zero emissions” to be when the ratio of landfill waste is 2% or less.
Amount of industrial waste generated
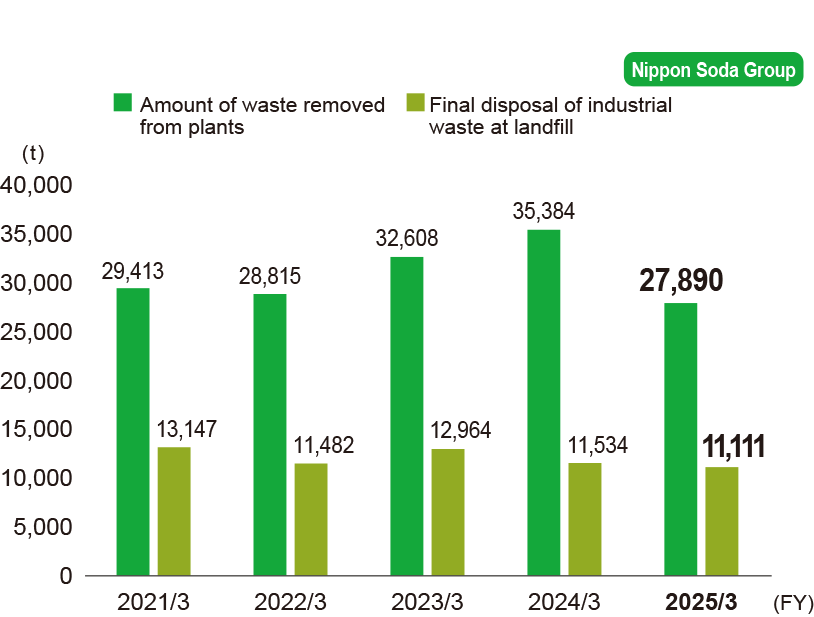
-
* Calculations cover the following.
Nippon Soda: Four plants and one research center
Domestic manufacturing group companies: Nisso Metallochemical Co., Ltd., Nisso Fine Co., Ltd., Shinfuji Kaseiyaku Co., Ltd.
Domestic non-manufacturing group companies: Sanwa Soko Co., Ltd., Nisso Kensetsu Co., Ltd., Nisso Green Co., Ltd.
Change in the amount of industrial waste generated
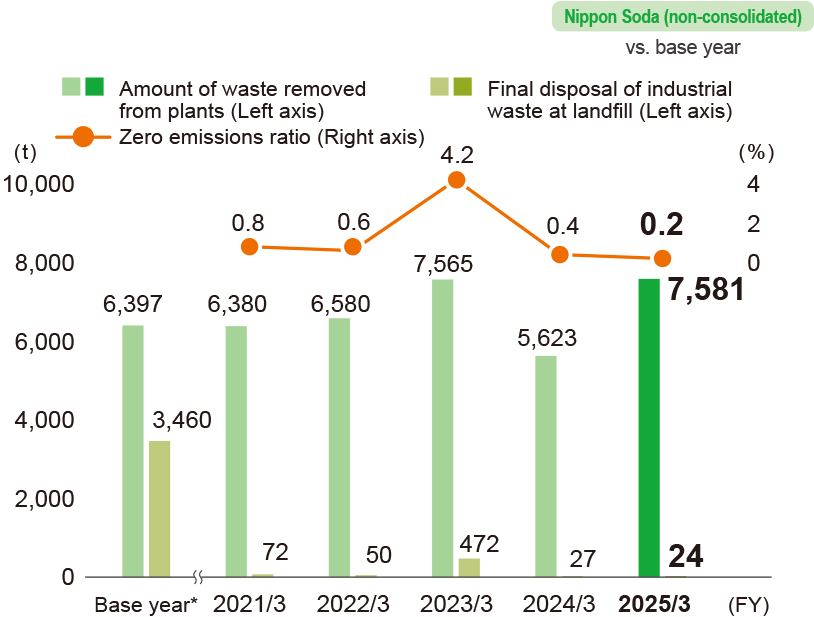
-
* Calculations cover Nippon Soda’s four plants and one research center.
Base year of the amount of waste removed from plants: FY 1996/3
Base year of the amount of final disposal at landfill: FY 1997/3
The amount of waste removed from plants does not include the waste sludge of the activated sludge process at Takaoka Plant (which is treated with microbial autolysis at an external facility).
In FY 2025/3, waste emissions increased owing to such factors as the disposal of excavated soil from the expansion project at the Nihongi Plant and the disposal of raw materials following the closure of the Mizushima Plant.
Amount of waste removed from plants
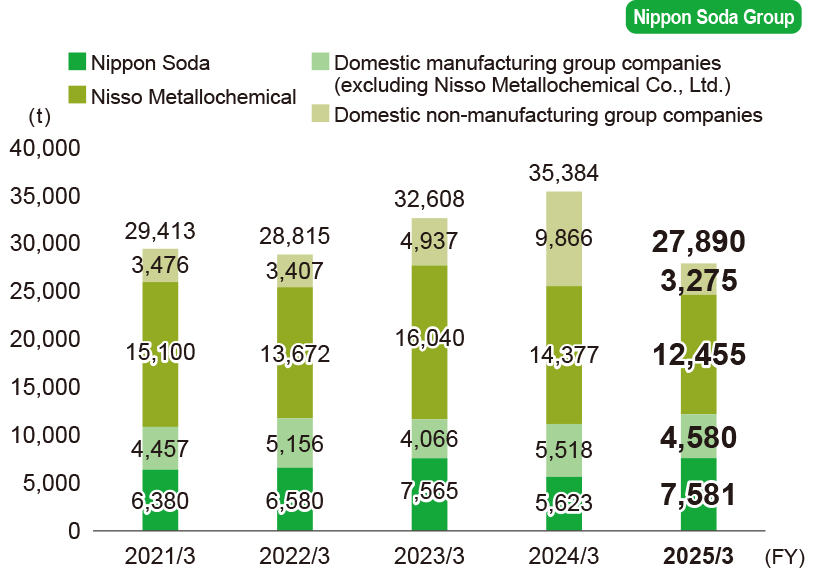
- * Calculations cover the following.
Nippon Soda: Four plants and one research center
Domestic manufacturing group companies: Nisso Metallochemical Co., Ltd., Nisso Fine Co., Ltd., Shinfuji Kaseiyaku Co., Ltd.
Domestic non-manufacturing group companies: Sanwa Soko Co., Ltd., Nisso Engineering Co., Ltd., Nisso Kensetsu Co., Ltd., Nisso Green Co., Ltd.
Final disposal of industrial waste at landfill
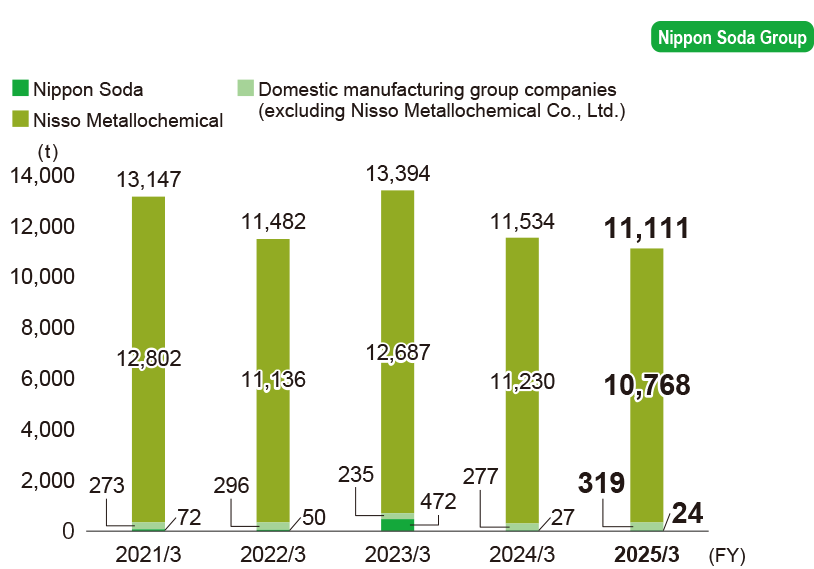
-
* Calculations cover the following.
Nippon Soda: Four plants and one research center
Domestic manufacturing group companies: Nisso Metallochemical Co., Ltd., Nisso Fine Co., Ltd., Shinfuji Kaseiyaku Co., Ltd.
PCB (polychlorinated biphenyl) waste
Each Nippon Soda site properly stores and manages condensers, transformers, mercury lamp ballasts, and other items which contain PCBs and disposes of them appropriately and systematically in accordance with the Act on Special Measures concerning Promotion of Proper Treatment of PCB Wastes, which was revised in 2016.
Creating a circular economy society through public-private partnership
Bandai Town (Yama District, Fukushima Prefecture) is actively working toward decarbonization and sustainable community development. The town has signed a comprehensive partnership agreement with local businesses, including Nisso Metallochemical Co., Ltd., to collaboratively promote the establishment of a circular economy society. Under this agreement, Nisso Metallochemical Co., Ltd. aims to contribute to the town's development by participating in waste reduction and resource recycling initiatives within Bandai Town. This initiative, which leverages the agility unique to small municipalities, is expected to serve as a model case that can be implemented in similar regions throughout Japan.
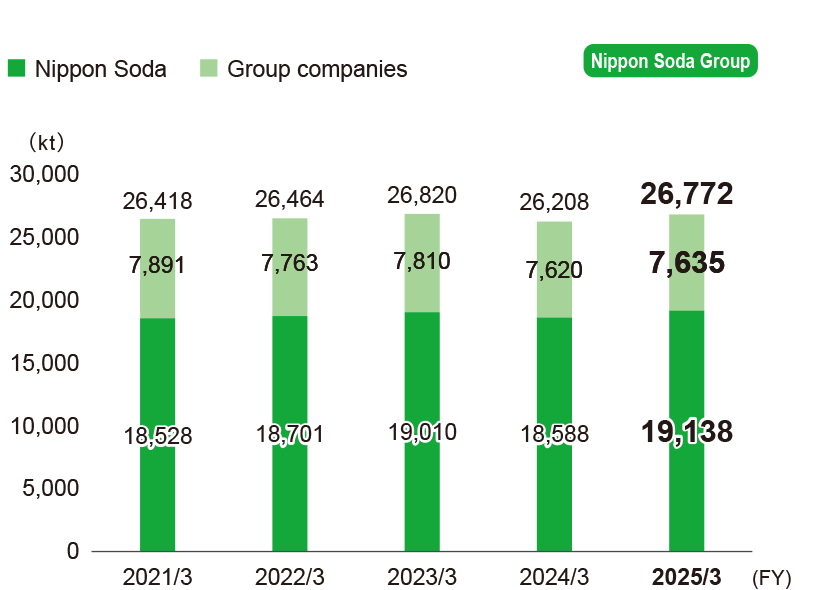
Major environmental impact data
The environment impacts of Nippon Soda’s four major plants in Japan in FY 2025/3 are shown in the figure below:
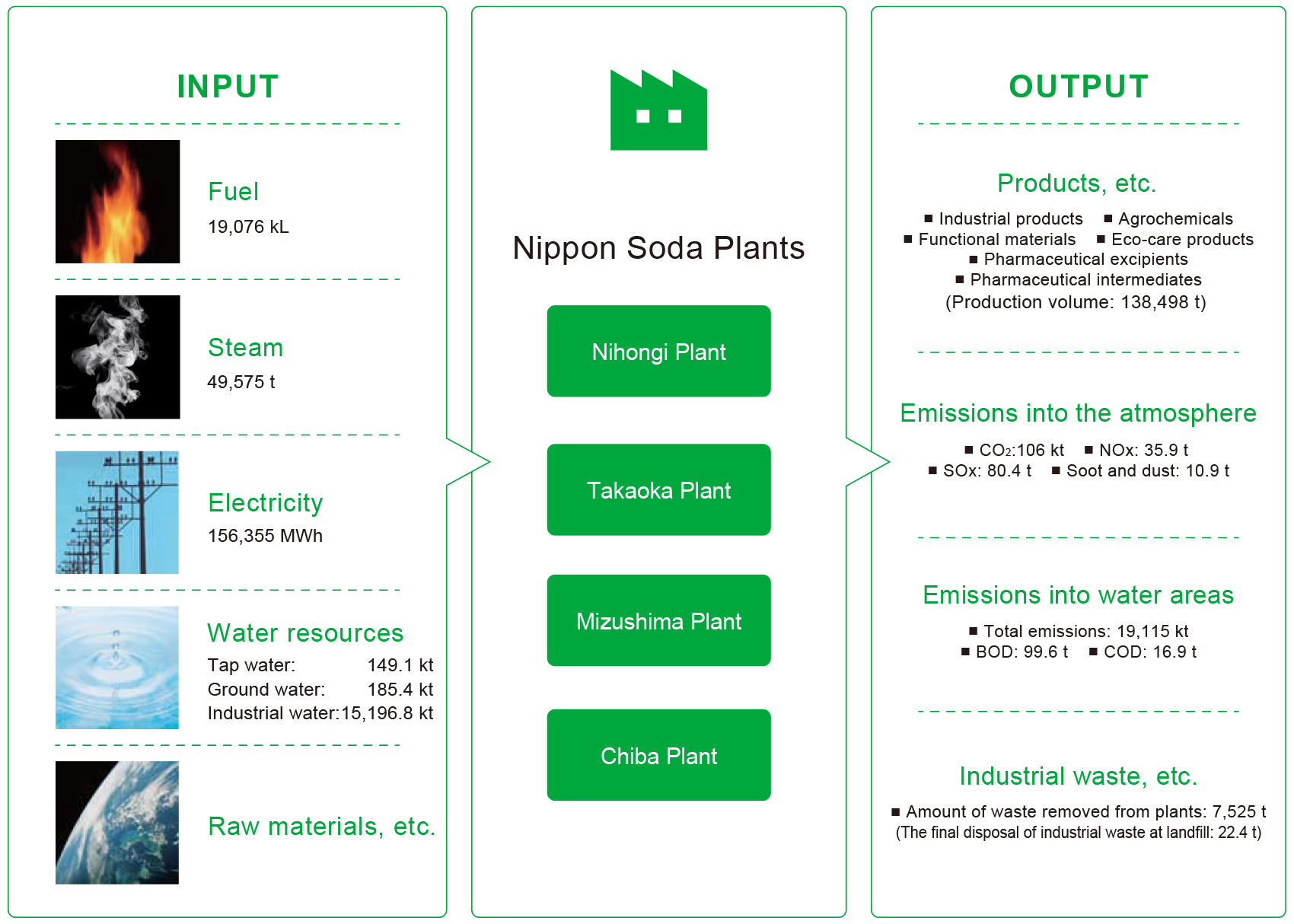
Atmosphere and Water Quality Conservation
Nippon Soda implements various measures to protect the atmosphere and water quality, such as reducing emissions of chemical substances subject to the PRTR system and reducing emissions of harmful substances into rivers and other bodies of water, in accordance with the Air Pollution Control Act, the Water Pollution Prevention Act, and the latest regulatory trends.
Reduction of chemical substances specified by the PRTR System
We are making efforts to reduce emissions of Class I Designated Chemical Substances specified by the PRTR System, one of two sections contained in the Act on Confirmation, etc. of Release Amounts of Specific Chemical Substances in the Environment and Promotion of Improvements to the Management Thereof.
Emissions of substances specified by the PRTR system
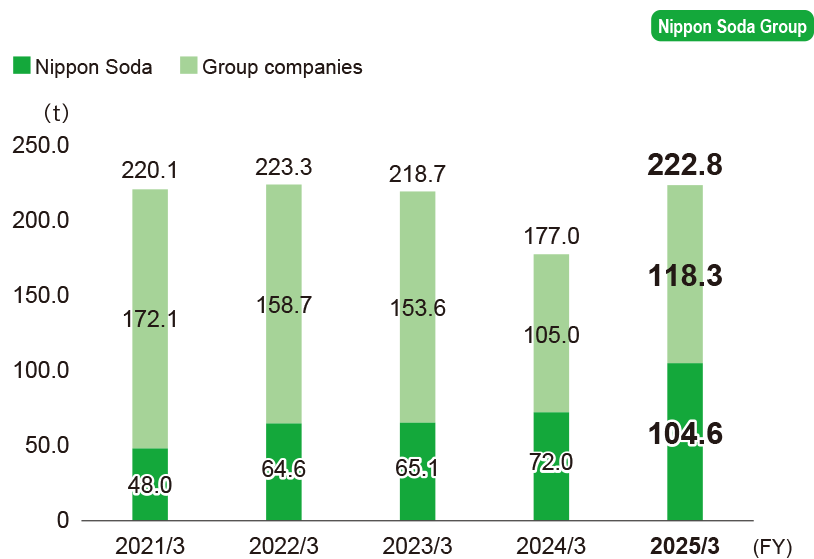
-
* Calculations cover the following.
Nippon Soda: Four plants and one research center
Domestic manufacturing group companies: Nisso Metallochemical Co., Ltd., Nisso Fine Co., Ltd.
Reduction of emissions of harmful substances into the atmosphere
Twelve chemicals among those categorized as priority substances under the Air Pollution Control Act are designated as voluntarily controlled chemical substances by the Japan Chemical Industry Association (JCIA). Of the twelve chemicals, the Company currently handles the following six substances: chloroform, dichloromethane, 1,2-dichloroethane, ethylene oxide, 1,3-butadiene and benzene. We are implementing measures to reduce the emissions of these six substances.
Atmospheric emissions of main voluntarily controlled chemical substances (aimed at reducing emissions of VOCs)
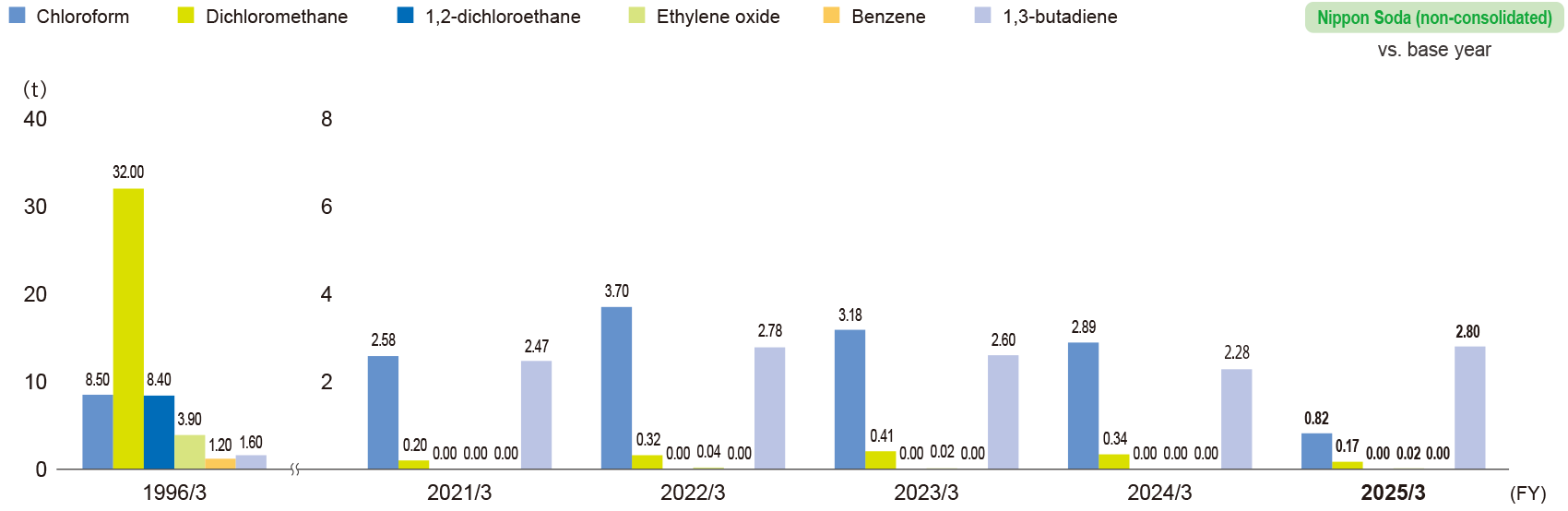
- * Calculations cover Nippon Soda’s four plants and one research center.
Reduction of air pollutant emissions
Nippon Soda promotes the reduction of emissions of sulfur oxide (SOx), nitrogen oxide (NOx), and soot and dust. Emissions of these substances from stationary sources are controlled under the Air Pollution Control Act.
Amount of emissions of substances subject to the Air Pollution Control Act
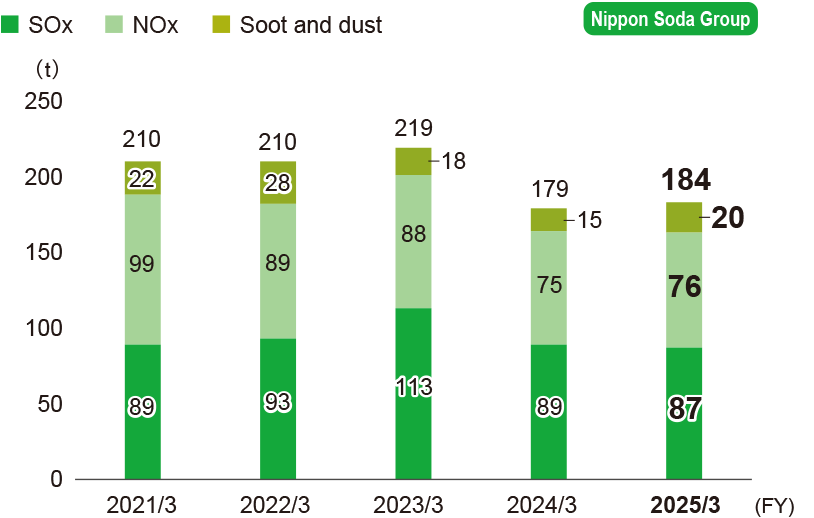
-
* Calculations cover the following.
Nippon Soda: Four plants
Domestic manufacturing group companies: Nisso Metallochemical Co., Ltd., Nisso Fine Co., Ltd.,
Change in the amount of emissions of substances subject to the Air Pollution Control Act
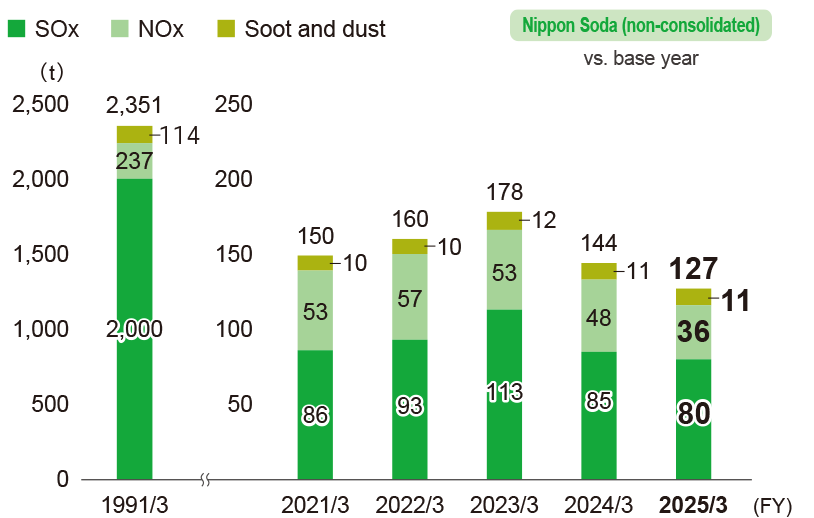
- * Calculations cover Nippon Soda’s four plants.
Reduction of wastewater discharge and harmful substance emissions into rivers and other bodies of water
Nippon Soda has made its voluntary standards stricter than the national regulatory values and the standard values agreed with local municipalities. Based on these strict values, we manage water quality through the monitoring of pollutants and purification at wastewater treatment plants.
Total volume of wastewater
- * Calculations cover the following.
Nippon Soda: Four plants and one research center
Domestic manufacturing group companies: Nisso Metallochemical Co., Ltd., Nisso Fine Co., Ltd.
Overseas manufacturing group companies: Nisso Namhae Agro Co., Ltd.
Total volume of wastewater and of BOD and COD
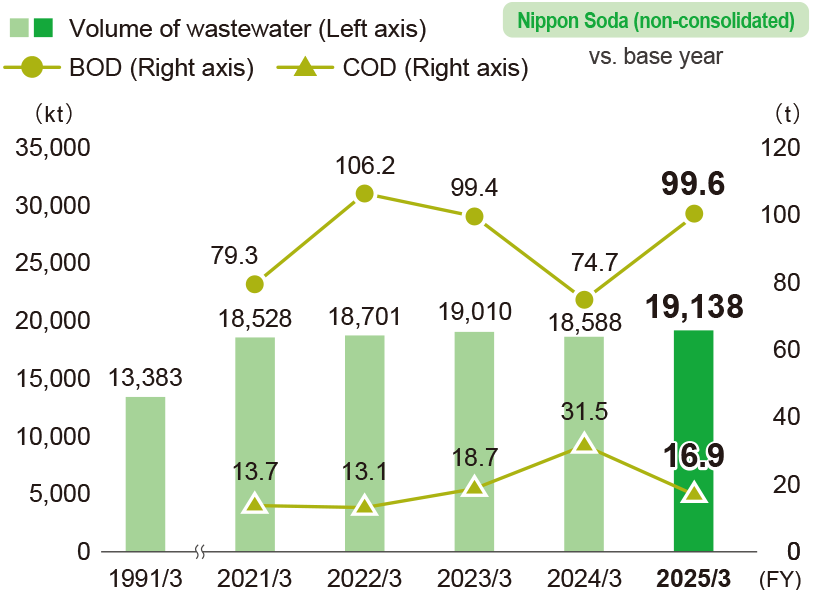
- * Calculations cover Nippon Soda’s four plants and one research center.
BOD associated with wastewater
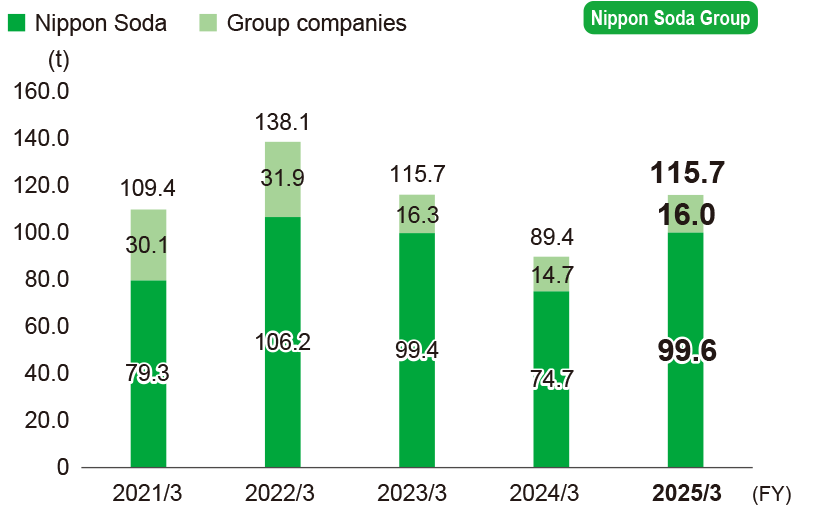
-
* Calculations cover the following.
Nippon Soda: Two plants
Domestic manufacturing group companies: Nisso Metallochemical Co., Ltd., Nisso Fine Co., Ltd.
COD associated with wastewater
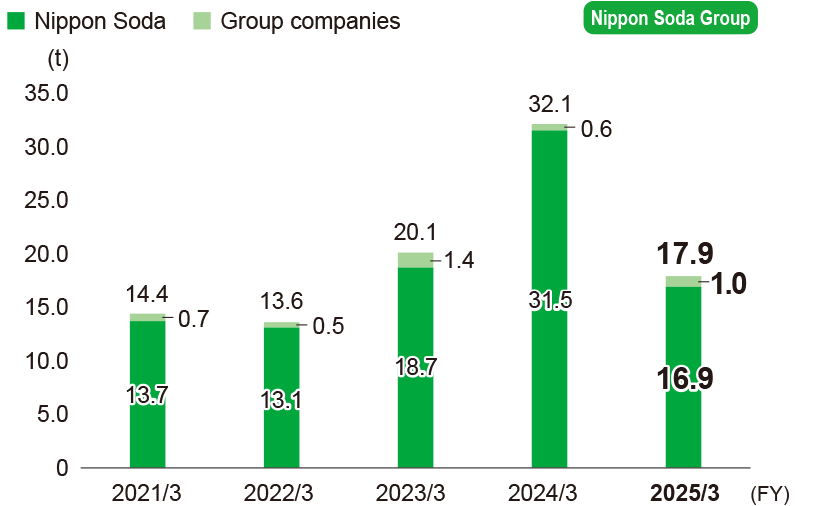
-
* Calculations cover the following.
Nippon Soda: Two plants
Domestic manufacturing group companies: Nisso Metallochemical Co., Ltd.
Preservation of Biodiversity
Nippon Soda has been taking measures to reduce its environmental burden, use water resources effectively, and prevent pollution of air, water, and soil, mainly in areas where its production sites are located. In recent years, we have added conservation of biodiversity as a priority issue and have been carrying out viable activities that can be implemented at each of our worksites.
Breeding of killifish originating from the Sakawa River system
(Research & Innovation Center [Odawara])
Odawara City, Kanagawa Prefecture, has been promoting protection activities for killifish, which are listed as an Endangered Species Category II by the Ministry of the Environment. In 1999, we conducted the Medaka-no Otosan Okasan Sato-oya Seido (“Killifish Fosterparent Program”), which involves working to protect their habitat and helping to pass their genes down to the next generation.
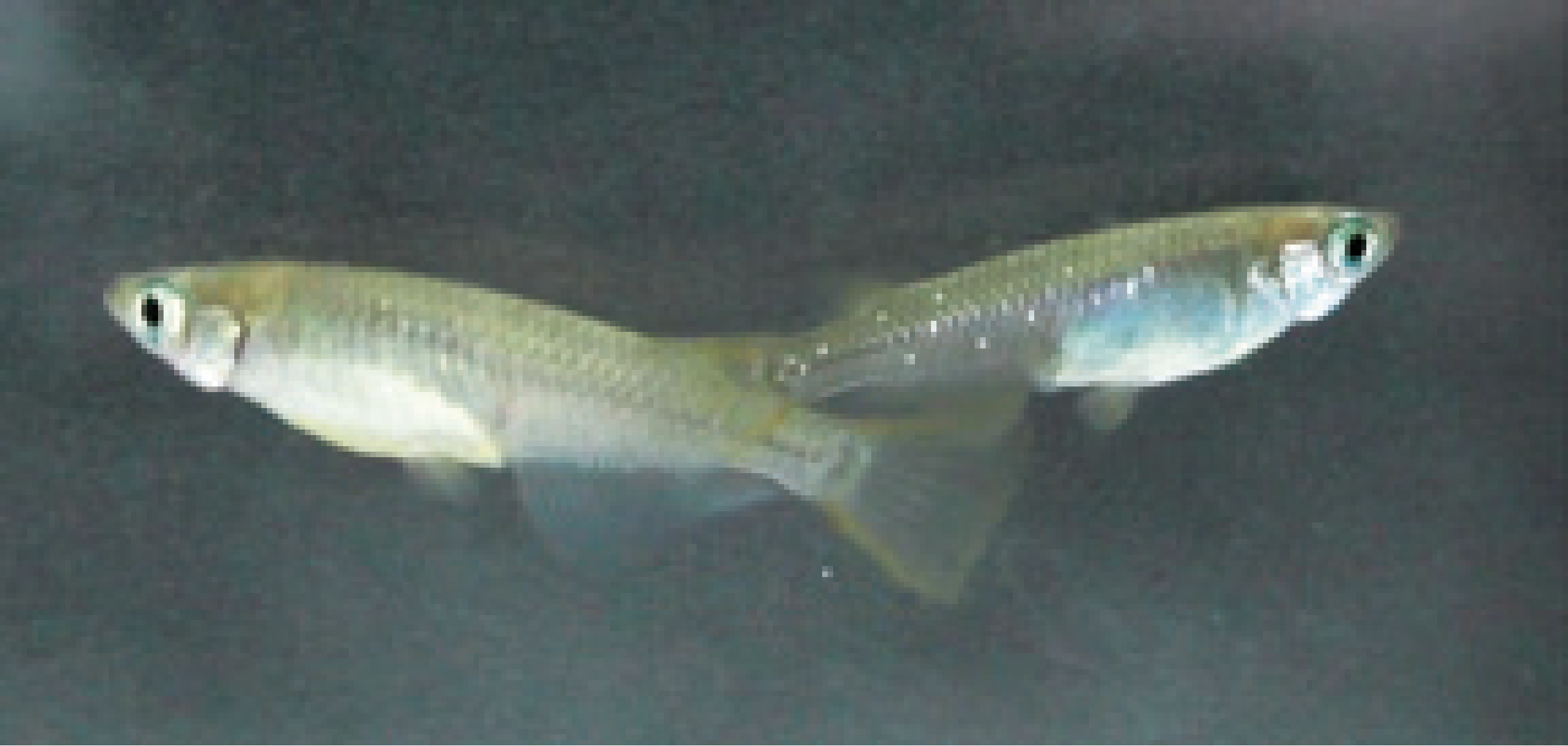



Breeding of killifish originating from the Sakawa River system
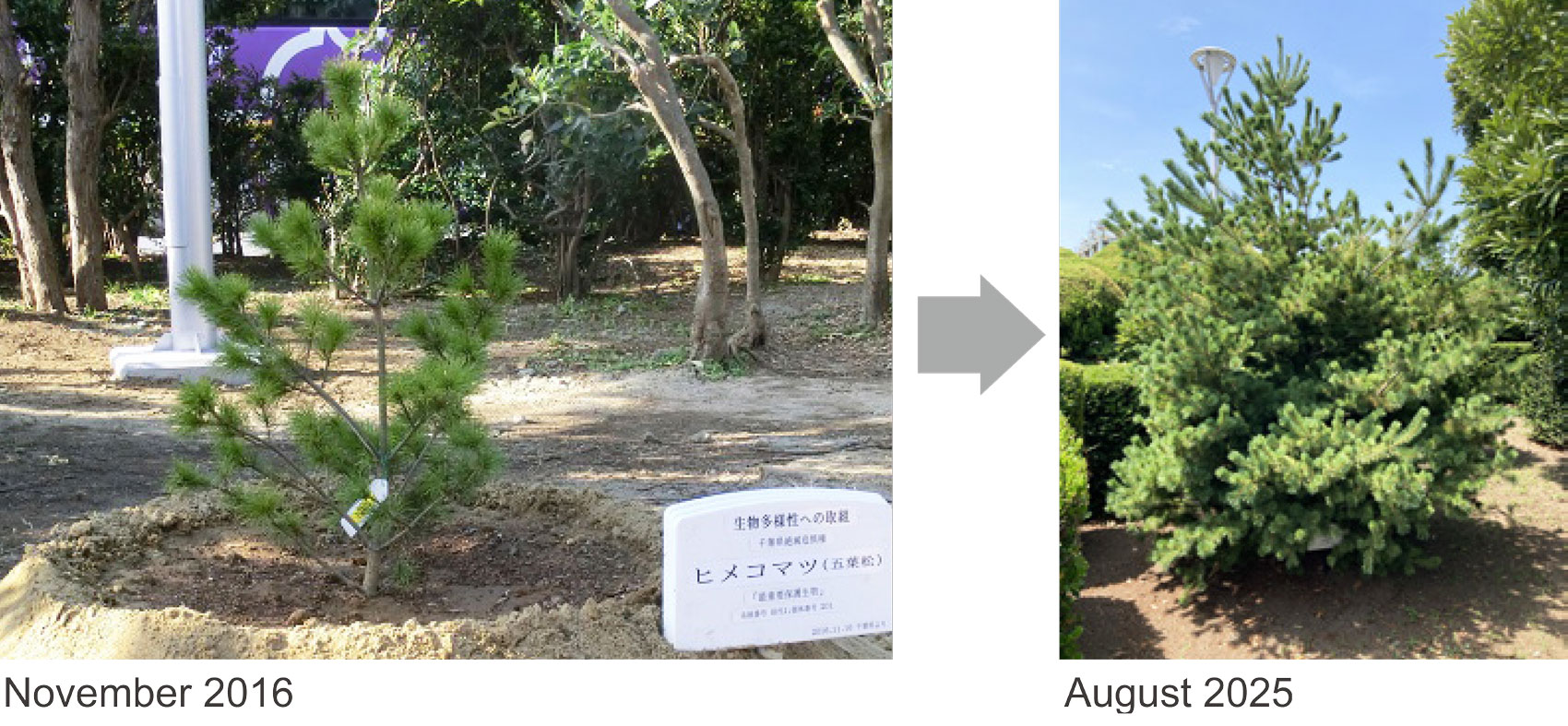
Supporting the protection of himekomatsu (Japanese white pine), a critically endangered species (Chiba Plant)
The Chiba Plant has continued with the Himekomatsu Supporter project which started in 2016 to protect himekomatsu, an endangered tree species in Chiba Prefecture.


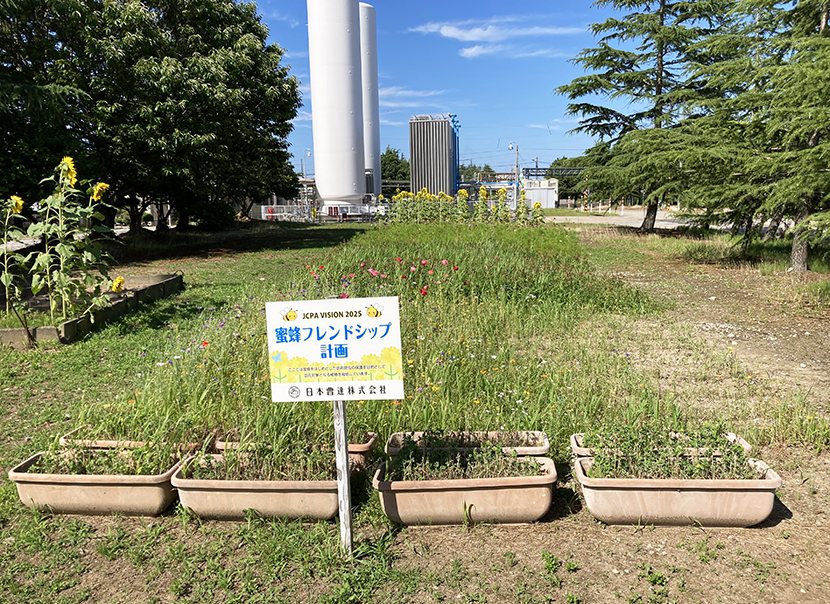
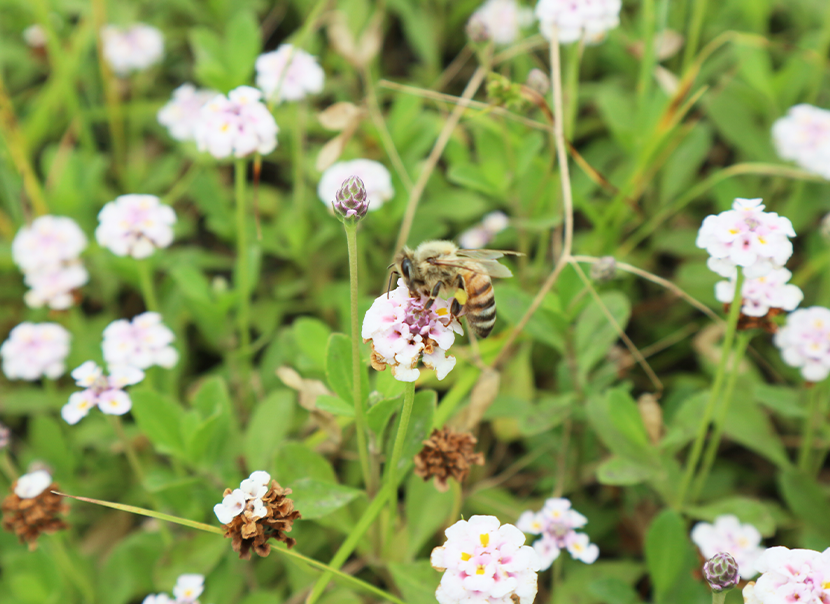
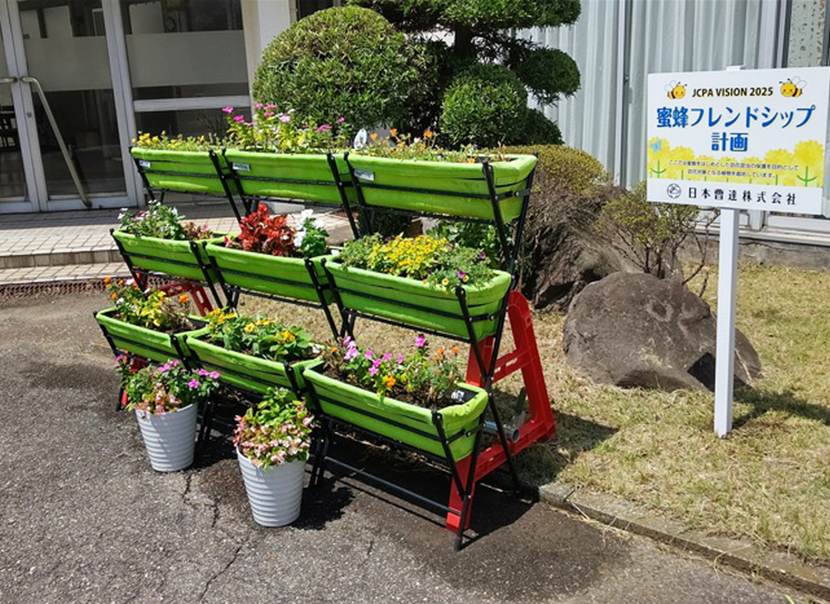
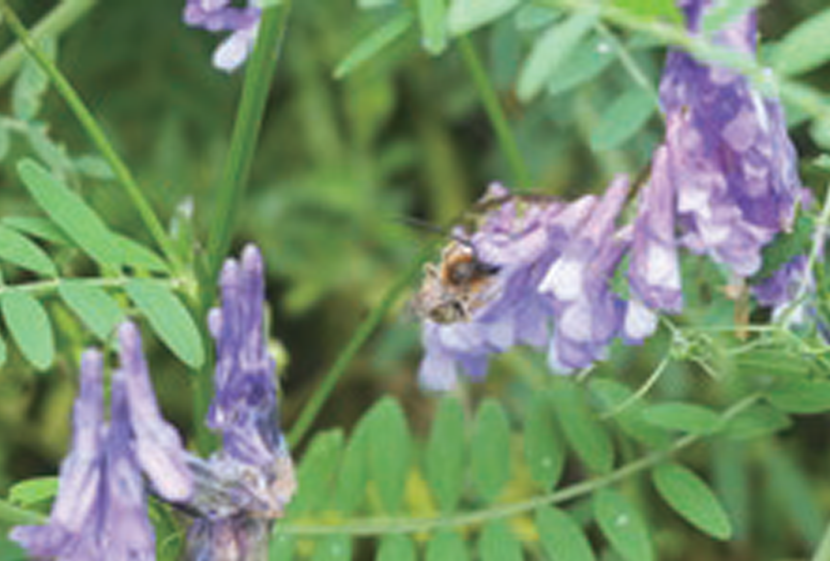
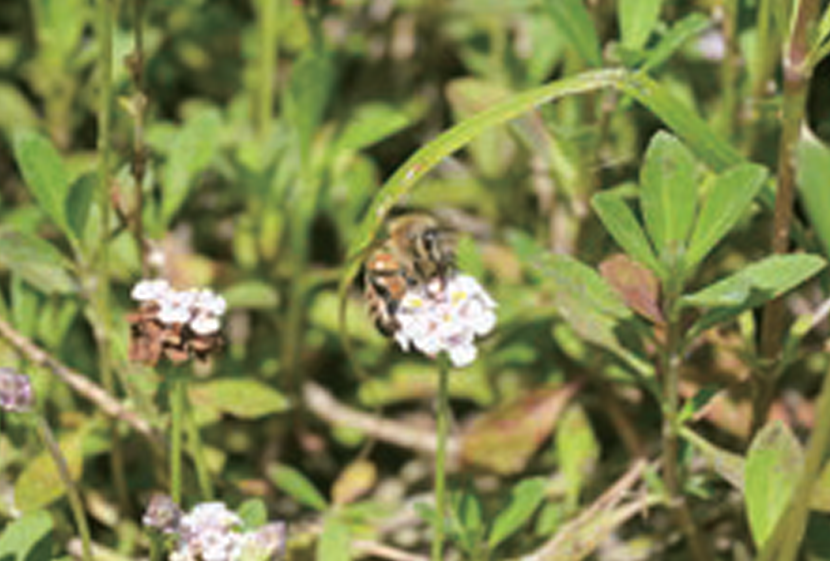
Participation in the CropLife JAPAN (CL Japan) Honeybee Friendship Plan
As one activity aimed at achieving its vision, since FY 2021/3 CL Japan* has operated the Honeybee Friendship Plan, through which it uses any available space at its member companies’ offices and land to grow plants for pollinating insects.
At Nippon Soda we fully support the Honeybee Friendship Plan and various efforts are underway at each of our worksites.
- * Name changed from Japan Crop Protection Association to CropLife JAPAN in May 2024






Environmental protection activities through the Nippon Soda Group Forest
On the occasion of the 100th anniversary of our establishment, we began initiatives to protect greenery and water sources as a contribution to the achievement of the SDGs. Nippon Soda established the Nippon Soda Group Forest within the Joetsu KUWADORI Community Forest in Joetsu City, Niigata Prefecture, the location of the Company’s origin, and continues to make donations to the National Land Afforestation Promotion Organization in order to contribute to the creation of a forest of biodiversity and environmental protection.
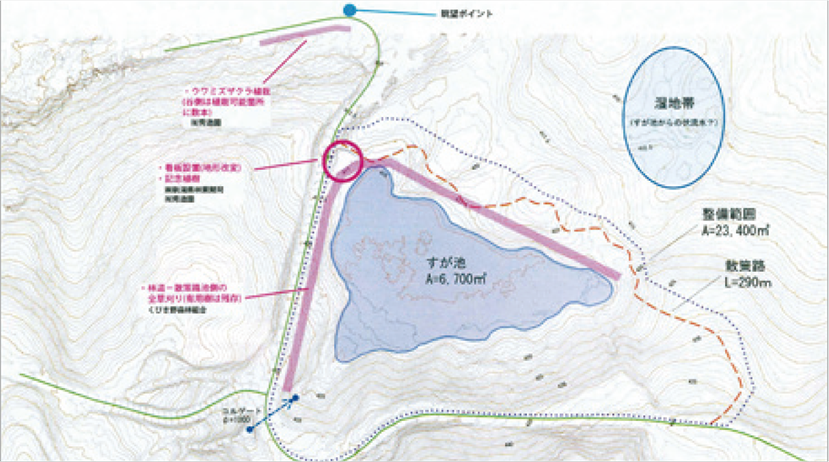
Nippon Soda Group Forest blueprint
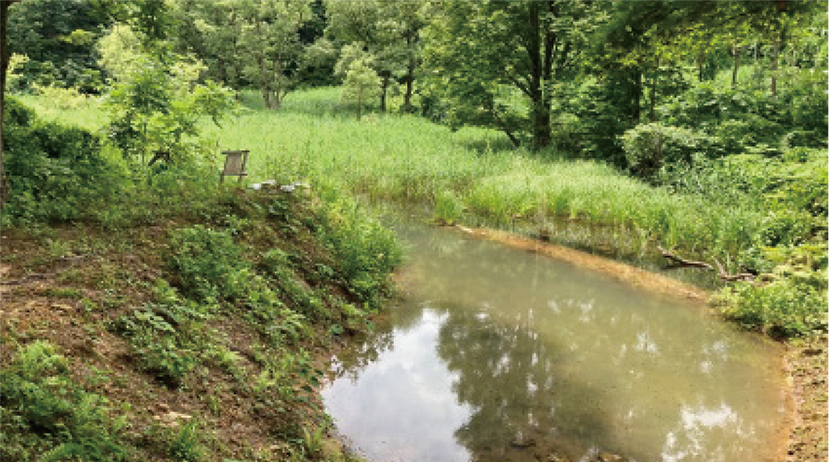

Water level at the Suga Lake
- 1. Environmental issues: Zero events
- 2. Climate change response (mitigation)
- 2-1. Manufacturing energy/production volume (intensity): Annual improvement of 1%
- 2-2. Logistics energy/logistics volume (intensity): Annual improvement of 1%
- 2-3.
- Reduction of greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions (Nippon Soda Group)
-
: FY 2026/3 Scope 1, 2, 3: Reduce by 20% or more (compared to FY 2014/3) : FY 2031/3 Scope 1, 2: Reduce by 42% or more (compared to FY 2023/3) Scope 3: Reduce by 25% or more (compared to FY 2023/3) : FY 2051/3 Scope 1, 2, 3: Achieve net-zero - : FY 2026/3 Scope 1, 2, 3: Reduce by 20% or more (compared to FY 2014/3)
- : FY 2031/3 Scope 1, 2: Reduce by 42% or more (compared to FY 2023/3)
- Scope 3: Reduce by 25% or more (compared to FY 2023/3)
- : FY 2051/3 Scope 1, 2, 3: Achieve net-zero
- 2-4. Fluorocarbon leaks: Elimination of issues related to leaks from equipment using fluorocarbons
- 2-5. Shift to renewable energy
: FY 2031/3: Shift to 59% renewable electricity
: FY 2051/3: Shift to 100% renewable electricity
- 3. Water resources conservation
- 3-1. Wastewater quality: Monitor water resources and promote efficient water use
- 3-2. Water usage: Annual 1% improvement in intensity of water consumption, wastewater discharge, and wastewater treatment volumes
- 3-3. Reduction of water risks: Annual 1% improvement in water consumption at manufacturing sites in high-water-risk areas
- 4. Waste
- 4-1. Amount of final disposal at landfill: Annual reduction of 3%
- 4-2. Continuation of zero emissions: 2% or less
- 4-3. Reduction of waste plastic, etc.
- 5. Emissions of harmful substances into the atmosphere: Annual reduction of 1%
- 6. Reduction of impact on biodiversity and ecosystems


